HTTP incoming source
The incoming-http source plugin showcases how you can send the Botkube command over HTTP instead of sending it from a communication platform.
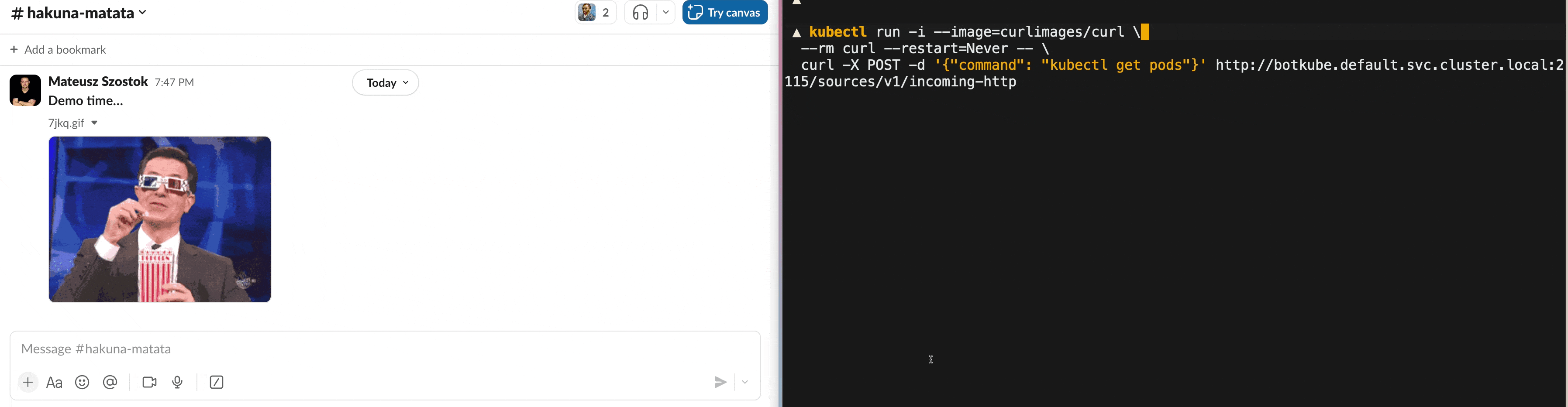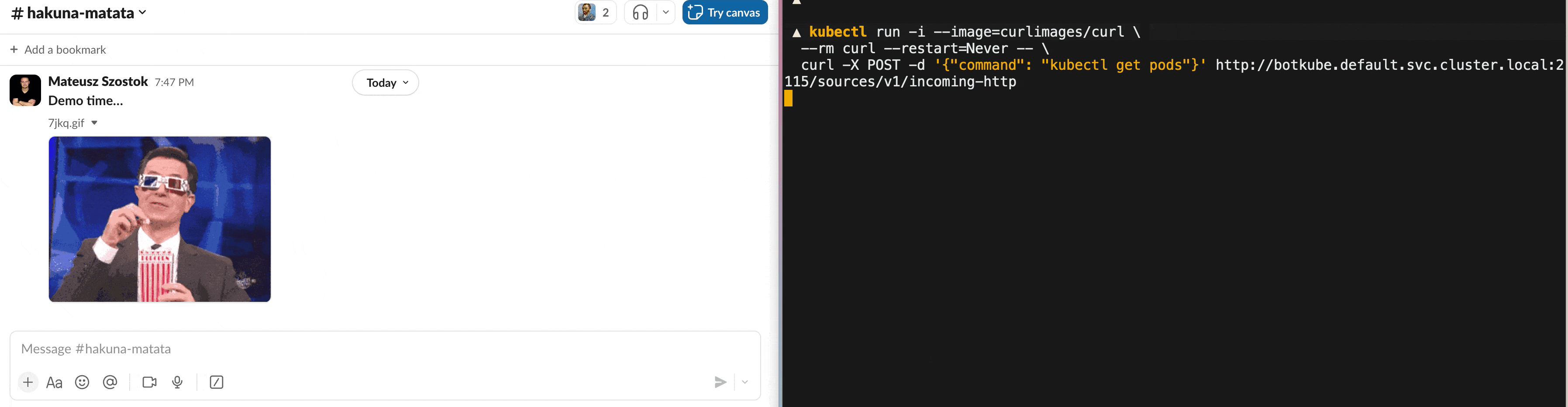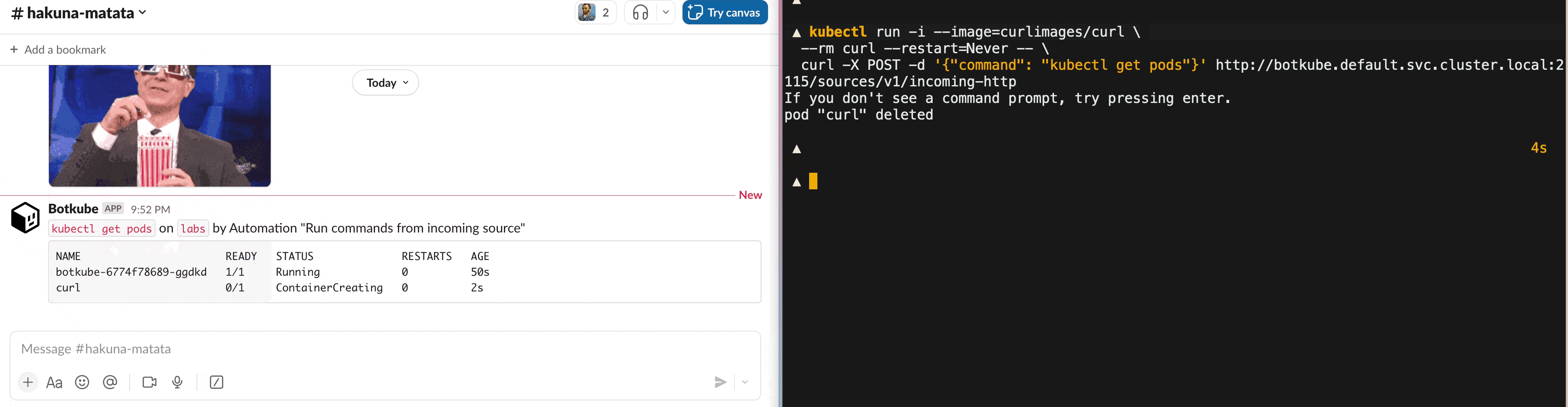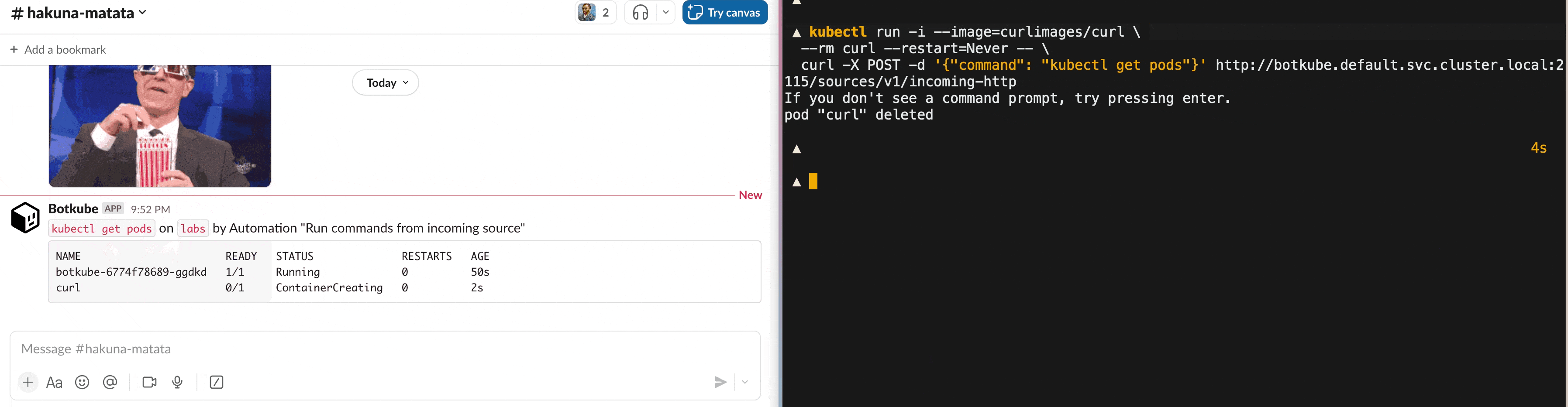
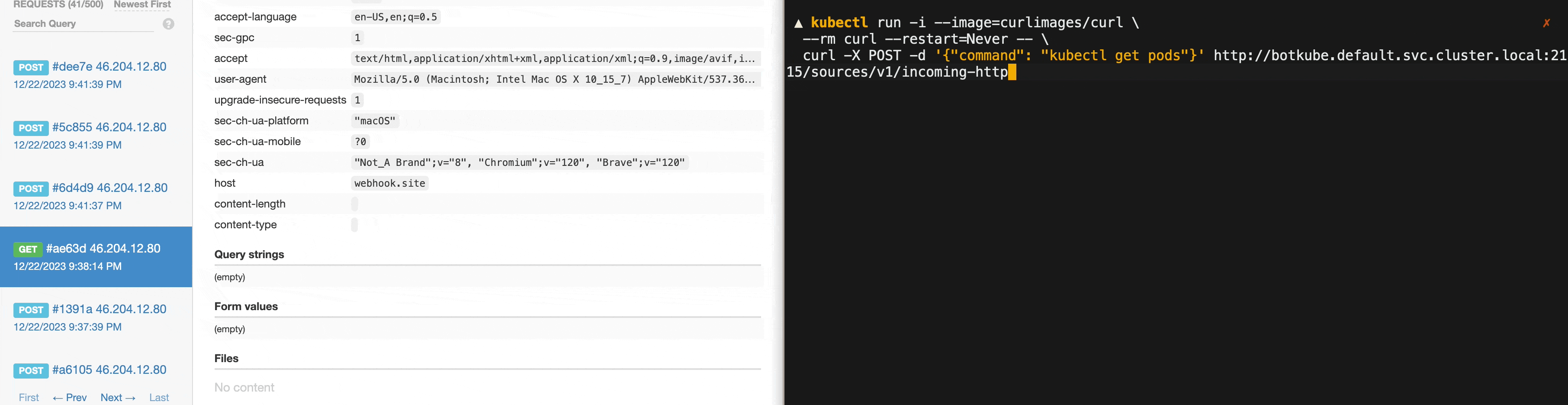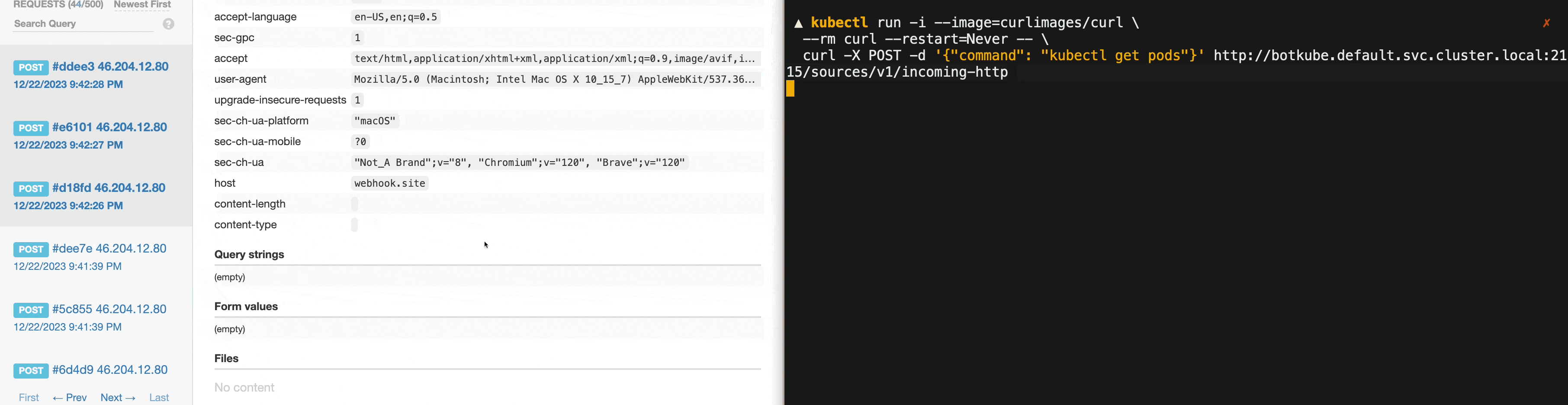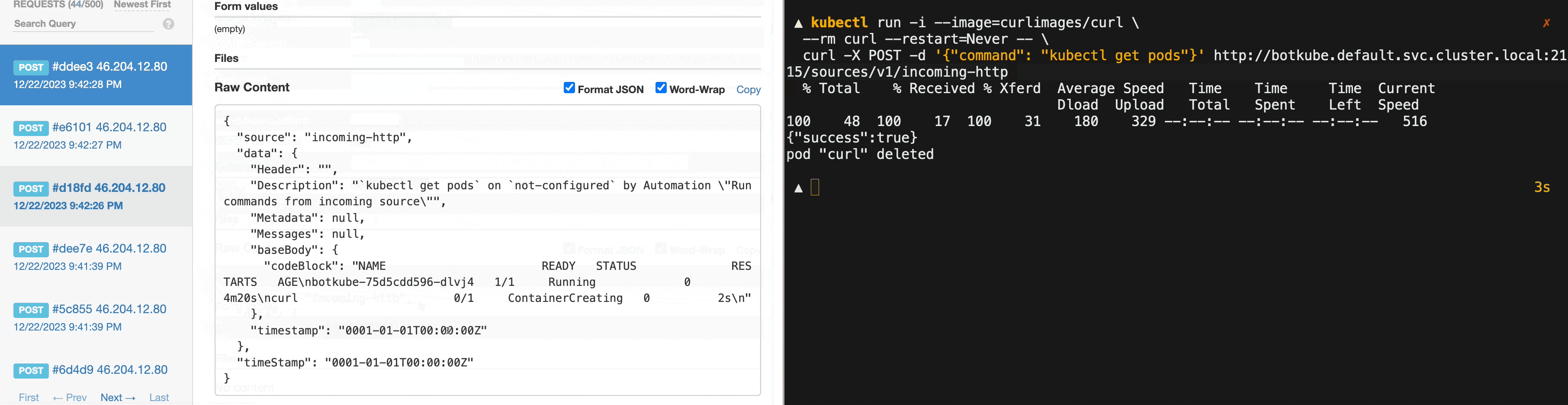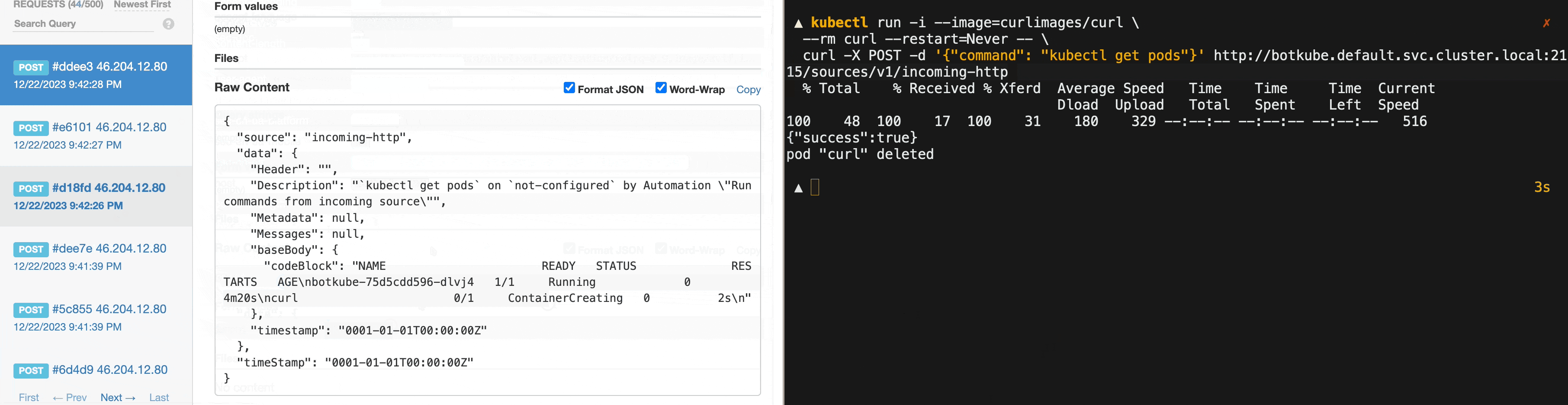
The sent command is executed by Botkube, and the output is posted on the configured communication platform channel. In this case, the output was posted on a Slack channel. However, it can be any communication platform that Botkube supports, even outgoing webhook, e.g.:
Tutorial
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster (e.g. k3d)note
To start a local cluster, run
k3d cluster create
Steps
Create the
config.yamlconfiguration file, with the following content:sources:
"incoming-http":
displayName: "HTTP incoming source"
mszostok/incoming-http:
enabled: true
actions:
"run-commands":
enabled: true
displayName: "Run commands from incoming source"
command: "{{ .Event.command }}"
bindings:
sources:
- incoming-http
executors:
- k8s-default-tools
executors:
k8s-default-tools:
botkube/kubectl:
enabled: true
botkube/helm:
enabled: true
settings:
clusterName: "labs"
plugins:
repositories:
mszostok:
url: https://github.com/mszostok/botkube-plugins/releases/download/v1.2.0/plugins-index.yamlInstall Botkube with the
config.yamlconfiguration file and configured communication platform.
- Webhook
- Socket Slack
helm repo add botkube https://charts.botkube.io
helm repo update
export WEBHOOK_URL={url} # e.g. obtain from https://webhook.site/
helm install botkube botkube/botkube --version v1.7.0 \
-f /tmp/config.yaml \
--set communications.default-group.webhook.enabled=true \
--set communications.default-group.webhook.url=${WEBHOOK_URL} \
--set communications.default-group.webhook.sources={"incoming-http"} \
--set image.repository=kubeshop/pr/botkube \
--set image.tag=1341-PR
helm repo add botkube https://charts.botkube.io
helm repo update
export SLACK_CHANNEL_NAME={channel_name} # without '#'
export SLACK_API_APP_TOKEN={token} # starts with 'xapp-1'
export SLACK_API_BOT_TOKEN={token} # starts with 'xoxb-'
helm install botkube botkube/botkube --version v1.7.0 \
-f /tmp/config.yaml \
--set communications.default-group.socketSlack.enabled=true \
--set communications.default-group.socketSlack.channels.default.name=${SLACK_CHANNEL_NAME} \
--set communications.default-group.socketSlack.appToken=${SLACK_API_APP_TOKEN} \
--set communications.default-group.socketSlack.botToken=${SLACK_API_BOT_TOKEN} \
--set communications.default-group.socketSlack.channels.default.bindings.sources={"incoming-http"} \
--set 'executors.k8s-default-tools.botkube/kubectl.enabled'=true \
--set 'executors.k8s-default-tools.botkube/helm.enabled'=true
To call the endpoint within the cluster, you can use the following command:
kubectl run -i --image=curlimages/curl \
--rm curl --restart=Never -- \
curl -X POST -d '{"command": "kubectl get pods"}' http://botkube.default.svc.cluster.local:2115/sources/v1/incoming-httpOtherwise, you need to port-forward the Botkube incoming webhook to your local machine:
kubectl port-forward svc/botkube 2115:2115and run the following command:
curl -X POST -d '{"command": "kubectl get pods"}' http://localhost:2115/sources/v1/incoming-http